BOC Sciences possesses advanced laboratory equipment and unique R&D expertise to support the development and manufacture of multiple chiral compounds ranging from chiral catalysts, chiral ligands, chiral auxiliaries to chiral resolution reagents. We strictly monitor our products during development and research processes to ensure our customers receive first-class services and products.
Stereocontrolled construction of organic molecules is one of the major challenges in organic synthesis. Therefore, development of new methods for the synthesis of enantiomerically enriched compounds is highly desirable. Chiral organocatalysts mainly play two roles in a reaction and these are the creation of an asymmetric environment in the reaction and the activation of the electrophile or the nucleophile or both. Based on the activation strategies of organocatalysts, their catalytic activity can be classified as non-covalent catalysis and covalent catalysis. Under the non-covalent catalysis category, thiourea-based organocatalysts have emerged as an efficient class of organocatalysts due to their unique dual hydrogen-bonding capacity.
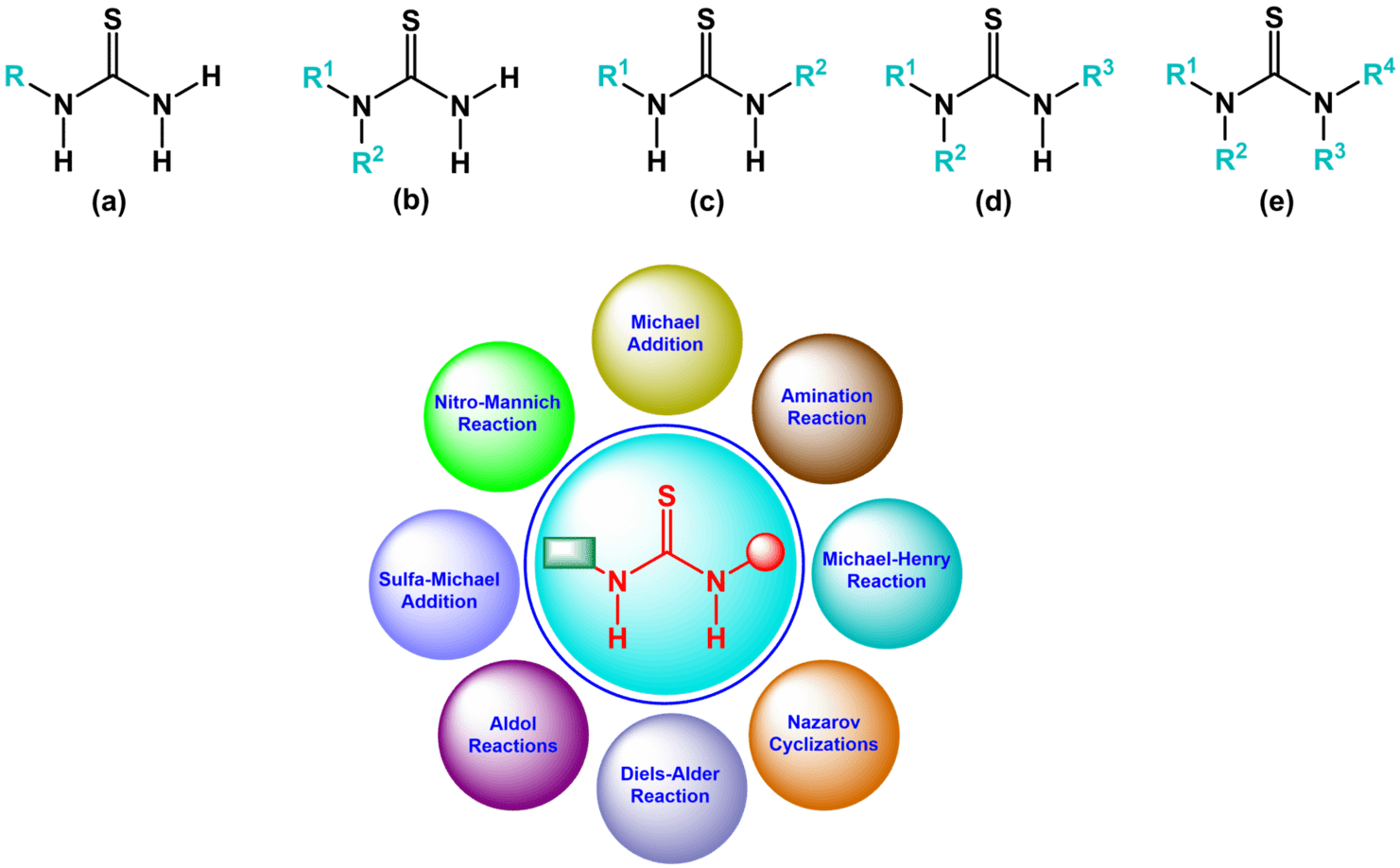 Fig. 1. Types of thioureas: (a) monosubstituted; (b) 1,1-disubstituted; (c) 1,3-disubstituted; (d) trisubstituted; (e) tetrasubstituted.
Fig. 1. Types of thioureas: (a) monosubstituted; (b) 1,1-disubstituted; (c) 1,3-disubstituted; (d) trisubstituted; (e) tetrasubstituted.
The replacement of the electronegative oxygen atom of urea by sulfur (with electronegativity comparable to carbon) results in a significant change of properties. Thioureas (thiocarbamides) exhibit higher acidity and are stronger hydrogen bond donors. This ability to participate in hydrogen bonding, which can be further modified by the appropriate substitution of nitrogen atoms, is essential for numerous applications of this class of organic compounds, mainly in organocatalysis and molecular recognition. Structurally thioureas can be classified depending on the number of substituents of nitrogen atom (Fig. 1). Not surprisingly, derivatives with one and two organic groups (either 1,1 or 1,3-disubstituted) are most common, though trisubstituted (with limited, but still preserved possibility to act as hydrogen bond donors) and fully substituted (mainly cyclic) thioureas are also prepared and used for various purposes.
The first thiourea were prepared about 150 years ago, and their chiral derivatives have been long known, but a great interest in the latter has arisen with the development of enantioselective organocatalysis. For almost 20 years they have been used as catalysts in organic synthesis, especially in stereoselective reactions. They also serve as valuable starting materials for the synthesis of heterocycles, and are used as ligands in coordination chemistry (particularly when additional donors are present in their molecules), as well as in the field of anion binding and recognition. A wide variety of chiral thiourea organocatalysts are known to accelerate various synthetically useful asymmetric organic transformations e.g., Michael addition, Nitro-Mannich reaction, Amination reaction, Sulfa-Michael addition, Domino aza Michael-Henry reaction, α-alkylation of aldehydes, Mannich-type reactions, Nazarov cyclizations, Diels-Alder reaction, intramolecular [5 + 2] cycloadditions, and vinylogous aldol reactions, etc.
References

Please click here to learn more about chiral technical support.
Suitable for your research and production needs. BOC Sciences provides the most comprehensive products and services. 24 hours customer support!



