| Catalog No. | Name | CAS | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCC-00024 | O-tert-Butyl-L-threonine | 4378-13-6 | |
| BCC-00407 | L-Alanine | 56-41-7 | |
| BCC-00730 | D-Alanine | 338-69-2 | |
| BCC-00733 | L-Threonine | 72-19-5 | |
| BCC-00736 | L-Tryptophan | 73-22-3 | |
| BCC-00875 | D-Threonine | 632-20-2 | |
| BCC-01186 | Tryptophan | 153-94-6 | |
| BCC-01199 | D-Phenylalanine | 673-06-3 | |
| BCC-01408 | O-TBDPS-D-Thr-N-Boc-L-tert-Leu-Diphenylphosphine | 1264520-63-9 |
BOC Sciences possesses advanced laboratory equipment and unique R&D expertise to support the development and manufacture of multiple chiral catalysts ranging from laboratory scale (mg to g) to industrial production (kg). We strictly monitor our products during development and research processes to ensure our customers receive first-class services and products.
Since the breakthrough in asymmetric catalysis made by William Knowles and his colleagues in 1970s, the demand for chiral compounds that are usually single enantiomers has escalated sharply. This was not only driven by the demands of the pharmaceutical industry but also by other applications, including agricultural chemicals, flavors, fragrances, and materials. Amino acids play key role both as building blocks of proteins and as intermediates in metabolism. The special structural characteristics of amino acids (containing both amine and carboxyl groups) determine their key roles in protein formation and serve as bifunctional asymmetric catalysts for stereoselective synthesis. The two functional groups can act as both acid and base to promote chemical transformations, similar to enzyme catalysis.
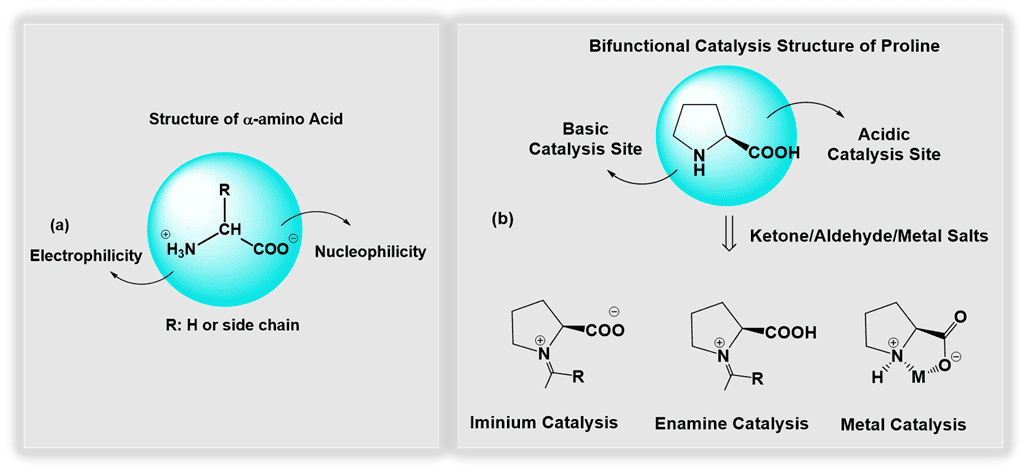 Fig. 1. (a) The structure of α-amino acid, and (b) potential catalysis intermediates of bifunctional proline-catalyzed transformations.
Fig. 1. (a) The structure of α-amino acid, and (b) potential catalysis intermediates of bifunctional proline-catalyzed transformations.
Although all amino acids contain both amine and carboxyl groups, proline, a secondary amino acid with a pyrrolidine-based structure, dominated early investigations. Its pyrrolidine ring determines its higher pKa value and unique nucleophilic reactivity compared to other primary amino acids. This facilitates the formation of iminium ions and enamines with carbonyl compounds more readily than most other amines, including cyclic examples such as piperidine. The synergistic interaction of carboxylate groups enhances and expands its application in organic catalysis. As a result, proline has been studied as an effective catalyst and investigated for several powerful asymmetric transformations, such as the Aldol, Mannich, and Michael reactions. Furthermore, modifications of amino acid include additional chiral centres and LUMO-activating groups such as ureas, thioureas and squaramides. In many cases, these modifications have resulted in improved organocatalytic properties in terms of stereocontrol and reaction scope. Both modified hydroxy proline and tert-leucine scaffolds have permitted to prepare organocatalysts for novel, concise and highly stereocontrolled synthesis of complex natural products.
Enantioselective organocatalysis, as a new asymmetric catalytic methodology, has produced a major impact on organic synthesis over the past 10 years and has built a bridge in the field of stereochemistry and drug active molecules. The development in organocatalysis initiated new methodologies for synthetic chemistry and has provided new strategies to construct bioactive molecules. Amino acids, as versatile catalysts, have been one of the most important classes of organocatalysis. And it is anticipated that the scale of amino acid catalysis will expand rapidly and future amino acid derivative catalysis will become a core asymmetric synthetic methodology. Typical procedures for amino acids catalytic reaction include direct catalytic asymmetric enolexo aldolizations, proline-catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol reactions, acyclic amino acid-catalyzed direct asymmetric aldol reactions (alanine), direct amino acid-catalyzed asymmetric synthesis of sugars, direct mannich reaction with acetone as nucleophile catalyzed by (S)-proline, ect.
References

Please click here to learn more about chiral technical support.
Suitable for your research and production needs. BOC Sciences provides the most comprehensive products and services. 24 hours customer support!



