Chiral analysis refers to the characterization of chiral molecules through a series of modern analytical instruments and methods. With advanced instruments and first-class technology, BOC Sciences can provide high-quality regulatory-driven chiral analysis services. Our chiral analysis experts only need a small amount of racemate or single isomer to obtain accurate and comprehensive analysis data, such as chiral purity and enantiomeric excess.
Conventional detectors can be used to detect chiral compounds. But in recent years, optically active detectors for chromatography have also been commercialized. The standard-compliant analysis laboratory of BOC Sciences is equipped with a series of advanced instruments for chiral analysis and identification.
HPLC has good reproducibility, selectivity, sensitivity, and rapidity, and its stationary phase has a wide selection range, which is suitable for the analysis of chiral compounds with strong polarity and poor thermal stability. It may also help improve the detection sensitivity of UV or fluorescence detectors.
For example
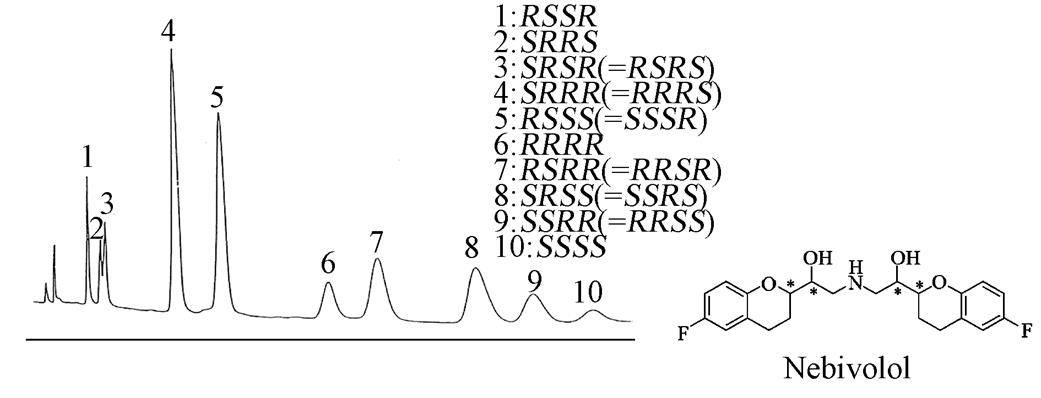 Fig.1 HPLC analysis of nebivolol (Dingene, J. 1994)
Fig.1 HPLC analysis of nebivolol (Dingene, J. 1994)
SFC is a new chromatographic technique. Since SFC uses supercritical fluid as the mobile phase, the mass transfer resistance is small, and the analysis and detection can be carried out quickly and efficiently. On the other hand, because the density of the supercritical fluid is similar to the liquid, SFC is similar to HPLC and is suitable for analysis of chiral compounds with low volatility, poor thermal stability and high relative molecular mass.
Compared with other analytical methods, gas chromatography (GC) can obtain more accurate results in a shorter time, and it has a stronger recognition ability. When used in combination with mass spectrometry (MS), liquid chromatography (LC), etc., it can also perform accurate quantitative and qualitative analysis of the measured unknown substances. The sample tested must be thermally stable and highly volatile.
CE has been widely used in chiral analysis due to its short analysis time, high sensitivity, small amount of mobile phase and a wide selection of chiral reagents. Cyclodextrin and its derivatives are the most common chiral selectors in this method.
For example
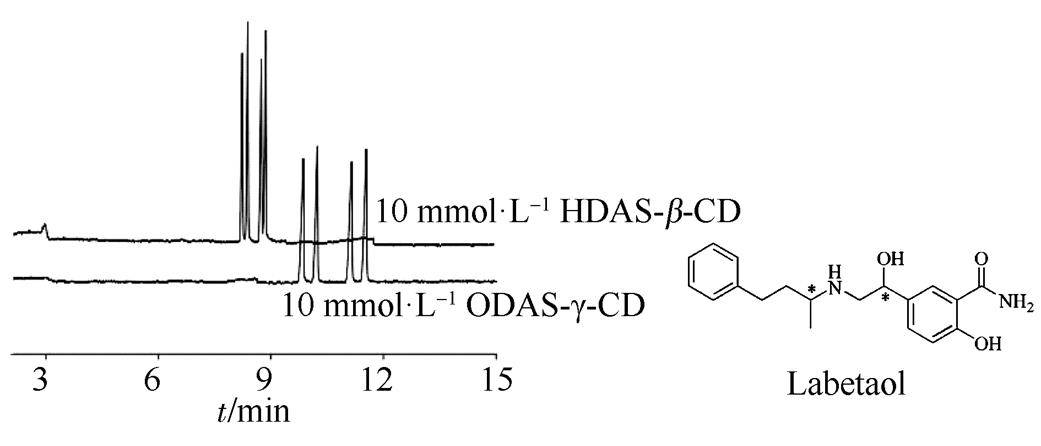 Fig.2 CE analysis of labetalol (Goel,T.V. et al, 2004)
Fig.2 CE analysis of labetalol (Goel,T.V. et al, 2004)
NMR converts enantiomers into diastereomers, or provides a chiral environment to make the nuclear magnetic resonance signals of the two enantiomers different, and then performs chiral analysis, such as detecting the content of S-type impurities in the R-isomer. The chemical shift reagents commonly used in this method are complexes of chiral rare earth ions.
References: